Open up a terminal window.
Firstly, Create a directory new name terminal
mkdir JenkinsChange the directory / Jenkins
cd JenkinsCreate another DockerFile and write nano Dockerfile in a terminal
sudo nano DockerfileBuild and Run
sudo docker build -t jenkins:lastest
sudo docker run -p 8080 -d -v var/jenkins_home/docker:var/jenkins_home/docker
# GNU nano 4.8 Dockerfile
FROM jenkins/jenkins:lts
#Switch to the root user to install additional packages
USER root
# Install prerequisites and Docker
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
RUN curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | apt-key add -
RUN add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y docker-ce
# Switch back to the Jenkins user
USER jenkins
# Expose Jenkins web interface on port 8080
EXPOSE 8080
# Start Jenkins
CMD ["/usr/local/bin/jenkins.sh"]
sudo docker ps -a
DESKTOP-TQ2GRMA:~$ sudo docker exec -it 7c7 bash
Sudo password for jenkins
Accessing the Jenkins home directory
You can access the Jenkins home directory, to check the details of a Jenkins build in the workspace subdirectory, for example.
If you mapped the Jenkins home directory (/var/jenkins_home) to one on your machine’s local file system, for example, in the docker run … command above, access the directory contents through your machine’s usual terminal/command prompt.
If you specified the --volume jenkins-data:/var/jenkins_home option in the docker run … command, access the contents of the Jenkins home directory through your container’s terminal/command prompt using the docker container exec command:
docker container exec -it <docker-container-name> bash
As per the previous section, get your <docker-container-name> using the docker container ls command. If you specified the --name jenkins-blueocean option in the docker container run … the command above (refer to Accessing the Jenkins/Blue Ocean Docker container if needed), use the docker container exec command:
docker container exec -it Dockerfile bash
Post-installation setup wizard
After downloading, installing and running Jenkins using one of the procedures above (except for installation with Jenkins Operator), the post-installation setup wizard begins.
This setup wizard takes you through a few quick "one-off" steps to unlock Jenkins, customize it with plugins and create the first administrator user through which you can continue accessing Jenkins.
Unlocking Jenkins
When you first access a new Jenkins instance, you are asked to unlock it using an automatically-generated password.
Browse to
http://localhost:8080(or whichever port you configured for Jenkins when installing it) and wait until the Unlock Jenkins page appears.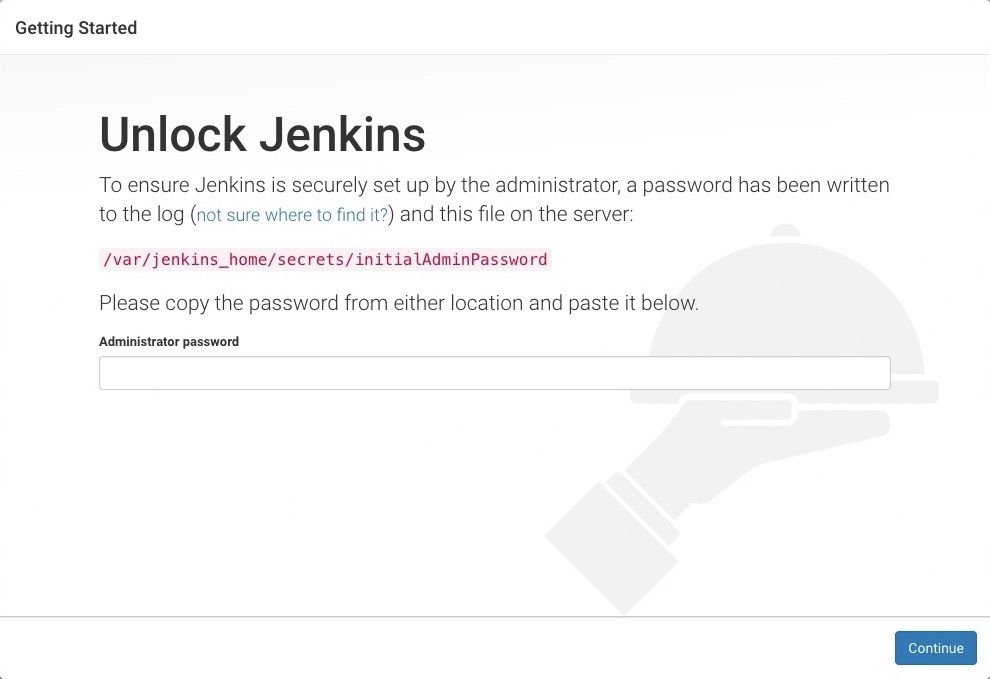
From the Jenkins console log output, copy the automatically-generated alphanumeric password (between the 2 sets of asterisks).
Note:
The command:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordwill print the password at the console.If you are running Jenkins in Docker using the official
jenkins/jenkinsimage you can usesudo docker exec ${CONTAINER_ID or CONTAINER_NAME} cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPasswordit to print the password in the console without having to exec into the container.sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword # cat /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword $ unlock your password for jenkins first level
On the Unlock Jenkins page, paste this password into the Administrator password field and click Continue.
Note:The Jenkins console log indicates the location (in the Jenkins home directory) where this password can also be obtained. This password must be entered in the setup wizard on new Jenkins installations before you can access Jenkins’s main UI. This password also serves as the default administrator account’s password (with username "admin") if you happen to skip the subsequent user-creation step in the setup wizard.
Then after login and password you will enter jenkins dashboard.

Just Click Configure and General despcrition

Soure code management
Click Git and Repositories?
Downward Repository URL : give url of github
Build Environment
export BUILD_NO=$BUILD_NUMBER echo "password" | sudo -S docker build -t sitename:$BUILD_NO .
Customizing Jenkins with plugins
After unlocking Jenkins, the Customize Jenkins page appears. Here you can install any number of useful plugins as part of your initial setup.
Click one of the two options shown:
Install suggested plugins - to Install the recommended set of plugins, which are based on the most common use cases.
Select plugins to install - to choose which set of plugins to initially install. When you first access the plugin selection page, the suggested plugins are selected by default.
If you are not sure what plugins you need, choose Install suggested plugins. You can install (or remove) additional Jenkins plugins at a later point in time via the Manage Jenkins > Plugins page in Jenkins. |
The setup wizard shows the progression of Jenkins being configured and your chosen set of Jenkins plugins being installed. This process may take a few minutes.
Creating the first administrator user
Finally, after customizing Jenkins with plugins, Jenkins asks you to create your first administrator user.
When the Create First Admin User page appears, specify the details for your administrator user in the respective fields and click Save and Finish.
When the Jenkins is ready page appears, click Start using Jenkins.
Notes:This page may indicate Jenkins is almost ready! instead and if so, click Restart.
If the page does not automatically refresh after a minute, use your web browser to refresh the page manually.
If required, log in to Jenkins with the credentials of the user you just created and you are ready to start using Jenkins!
